Electrical Formulas Chart Pdf

Electrical Formulae for Calculating Amps, Horsepower, Kilowatts, & KVA Use the chart in this calculation guide to find the formula you need according to the measure you will calculate.
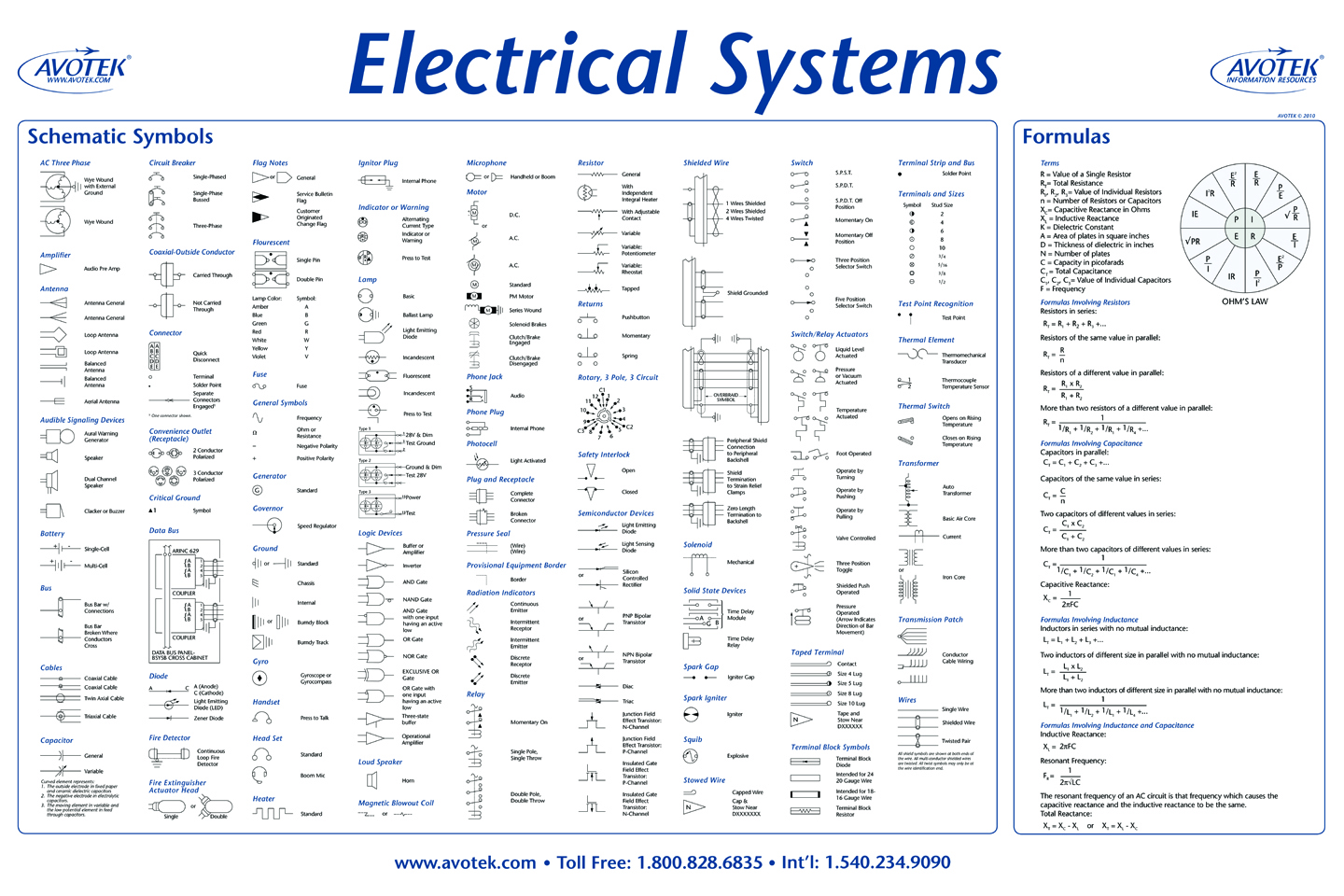
Electrical Equations Formulas Pdf
Electronics For Dummies Cheat Sheet From By Electronics is more than just schematics and circuits. By using various components, such as resistors and capacitors, electronics allows you to bend electric current to your will to create an infinite variety of gizmos and gadgets. In exploring electronics, use this handy reference for working with Ohm’s, Joule’s, and Kirchhoff’s Laws; making important calculations; determining the values of resistors and capacitors according to the codes that appear on their casings; and using a 555 timer and other integrated circuits (ICs). Important Formulas in Electronics With just a handful of basic mathematical formulas, you can get pretty far in analyzing the goings-on in electronic circuits and in choosing values for electronic components in circuits you design. Ohm’s Law and Joule’s Law Ohm’s Law and Joule’s Law are commonly used in calculations dealing with electronic circuits. These laws are straightforward, but when you’re trying to solve for one variable or another, it is easy to get them confused.
Electrical cheat sheet. Electrical Formulas and Calculations -E-Book - (2005) National Electrical Code. Basic Electrical pdf file. Electrical Formulas To Find Single Phase Two Phase -Four Wire Three Phase Amps when HP is known HP x 746. This chart was constructed using data from the.
Electrical Formulas List
The following table presents some common calculations using Ohm’s Law and Joule’s Law. In these calculations: V = voltage (in volts) I = current (in amps) R = resistance (in ohms) P = power (in watts) Unknown Value Formula Voltage V = I x R Current I = V/R Resistance R = V/I Power P = V x I or P = V 2/R or P = I 2R Equivalent resistance and capacitance formulas Electronic circuits may contain resistors or capacitors in series, parallel, or a combination.
Electrical Formulas
You can determine the equivalent value of resistance or capacitance using the following formulas: Resistors in series: Resistors in parallel: or Capacitors in series: or Capacitors in parallel: Kirchhoff’s Current and Voltage Laws Kirchhoff’s Circuit Laws are commonly used to analyze what’s going on in a closed loop circuit. Based on the principle of conservation of energy, Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) states that, at any node (junction) in an electrical circuit, the sum of currents flowing into that node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of that node, and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the sum of all voltage drops around a circuit loop equals zero.
For the circuit shown, Kirchhoff’s Laws tells you the following: KCL: I = I 1 + I 2 KVL: V battery – V R – V LED = 0, or V battery = V R + V LED Calculating the RC time constant In a resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit, it takes a certain amount of time for the capacitor to charge up to the supply voltage, and then, once fully charged, to discharge down to 0 volts. Circuit designers use RC networks to produce simple timers and oscillators because the charge time is predictable and depends on the values of the resistor and the capacitor.
If you multiply R (in ohms) by C (in farads), you get what is known as the RC time constant of your RC circuit, symbolized by T: A capacitor charges and discharges almost completely after five times its RC time constant, or 5 RC. After the equivalent of one time constant has passed, a discharged capacitor will charge to roughly two-thirds its capacity, and a charged capacitor will discharge nearly two-thirds of the way. Electronics: Reading Resistor and Capacitor Codes Electronics can sometimes be difficult to decipher.
By decoding the colorful stripes sported by many resistors and the alphanumeric markings that appear on certain types of capacitors, you can determine the nominal value and tolerance of the specific component. Resistor color codes Many resistor casings contain color bands that represent the nominal resistance value and tolerance of the resistor. You translate the color and position of each band into digits, multipliers, and percentages. The table that follows outlines the meaning of the resistor color bands.
Color 1st Digit 2nd Digit Multiplier Tolerance Black 0 0 x1 ±20% Brown 1 1 x10 ±1% Red 2 2 x100 ±2% Orange 3 3 x1,000 ±3% Yellow 4 4 x10,000 ±4% Green 5 5 x100,000 n/a Blue 6 6 x1,000,000 n/a Violet 7 7 x10,000,000 n/a Gray 8 8 x100,000,000 n/a White 9 9 n/a n/a Gold n/a n/a x0.1 ±5% Silver n/a n/a x0.01 ±10% Capacitor value reference In electronic circuits, the value of a capacitor can be determined by a two- or three-digit code that appears on its casing. The following table outlines values for some common capacitors. Marking Value nn (a number from 01 to 99) or nn0 nn picofarads (pF) 101 100 pF 102 0.001 µF 103 0.01 µF 104 0.1 µF 221 220 pF 222 0.0022 µF 223 0.022 µF 224 0.22 µF 331 330 pF 332 0.0033 µF 333 0.033 µF 334 0.33 µF 471 470 pF 472 0.0047 µF 473 0.047 µF 474 0.47 µF Capacitor tolerance codes In electronic circuits, the tolerance of capacitors can be determined by a code that appears on the casing. The code is a letter that often follows a three-digit number, for instance, the Z in 130Z. The following table outlines common tolerance values for capacitors. Note that the letters B, C, and D represent tolerances in absolute capacitance values, rather than percentages.
These three letters are used on only very small (pF range) capacitors. Code Tolerance B ± 0.1 pF C ± 0.25 pF D ± 0.5 pF F ± 1% G ± 2% J ± 5% K ± 10% M ± 20% Z +80%, –20%. Electronics: Integrated Circuit (IC) Pinouts The pins on an IC chip provide connections to the tiny integrated circuits inside of your electronics. To determine which pin is which, you look down on the top of the IC for the clocking mark, which is usually a small notch in the packaging but might instead be a little dimple or a white or colored stripe. By convention, the pins on an IC are numbered counterclockwise, starting with the upper-left pin closest to the clocking mark. So, for example, with the clocking notch orienting the chip at the 12 o’clock position, the pins of a 14-pin IC are numbered 1 through 7 down the left side and 8 through 14 up the right side.